Cervical radiculopathy is a condition caused by compression or irritation of cervical nerve roots, leading to neck pain, radiating arm pain, numbness, and weakness. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving mobility through targeted exercises and interventions.
1.1 Definition and Overview
Cervical radiculopathy is a condition characterized by compression or irritation of the cervical nerve roots, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the neck and arms. It often results from degenerative changes, herniated discs, or spinal instability. Physical therapy plays a central role in managing symptoms, focusing on exercises to improve mobility, strength, and posture. Techniques such as cervical traction, stretching, and manual therapy are commonly used to alleviate discomfort and restore function. This approach helps patients regain independence and reduce the need for surgical intervention, making it a cornerstone of conservative management.
1.2 Common Symptoms and Diagnosis
Cervical radiculopathy often presents with radiating pain from the neck to the arm, numbness, tingling, or weakness in specific dermatomal patterns. Symptoms may worsen with certain movements or prolonged postures. Diagnosis involves a detailed clinical examination, including neurological assessment to identify affected nerve roots. Imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, are commonly used to confirm nerve compression. Physical therapy evaluations focus on identifying limitations in range of motion, strength deficits, and postural abnormalities. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management and preventing progression of symptoms.
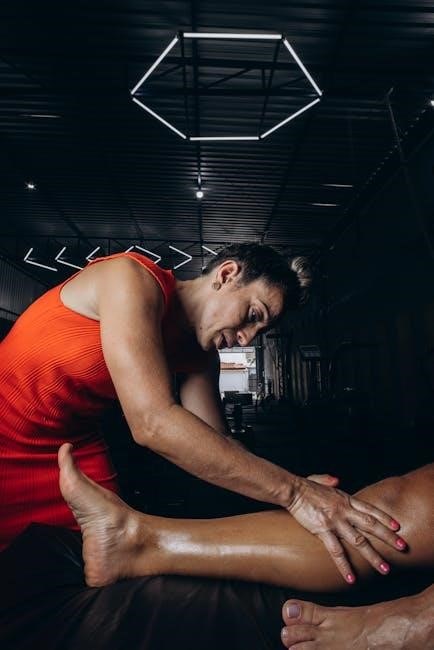

Physical Therapy Assessment and Treatment
Physical therapy assessment focuses on evaluating range of motion, strength, and posture. Treatment involves targeted exercises, manual therapy, and cervical traction to alleviate symptoms and improve function.
2.1 Role of Physical Therapy in Managing Cervical Radiculopathy
Physical therapy is a cornerstone in managing cervical radiculopathy, offering a conservative approach to reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore function. It addresses nerve compression through targeted exercises, manual therapy, and traction. By focusing on strengthening neck muscles, improving posture, and enhancing range of motion, physical therapy helps alleviate symptoms and prevents recurrence. It also educates patients on proper body mechanics and ergonomics, empowering them to manage their condition effectively and resume daily activities without aggravating their symptoms.
2.2 Key components of a Physical Therapy Program
A well-rounded physical therapy program for cervical radiculopathy includes pain management, manual therapy, and exercises tailored to individual needs. Stretching and strengthening exercises target cervical muscles and improve posture. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue work, relieve stiffness and nerve pressure. Education on proper ergonomics and body mechanics is also crucial to prevent recurrence. Progression of exercises ensures sustained improvement, focusing on functional activities to help patients return to daily life seamlessly.

Recommended Exercises for Cervical Radiculopathy
Exercises for cervical radiculopathy focus on stretching, strengthening, and improving posture to alleviate pain and restore function. They include cervical stretches, isometric exercises, and scapular stabilization techniques.
3.1 Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises are a cornerstone in managing cervical radiculopathy. They aim to relieve tension in the cervical spine and surrounding muscles, reducing nerve compression. Common stretches include the Sternocleidomastoid stretch, Upper Trapezius stretch, and Levator Scapulae stretch. These exercises help improve cervical range of motion and reduce radiating pain. Patients are often advised to perform gentle, sustained stretches for 20-30 seconds, avoiding sharp pain. Regular stretching can alleviate symptoms and improve functional mobility, making daily activities more comfortable. Proper technique is essential to ensure effectiveness and avoid further irritation.
3.2 Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises are vital for addressing cervical radiculopathy by enhancing the stability and support of the cervical spine. These exercises target key muscles such as the deep cervical flexors, scapular stabilizers, and upper trapezius. Isometric neck exercises, chin tucks, and scapular wall slides are commonly recommended. They help improve posture, reduce strain on the cervical spine, and prevent further nerve irritation. Performing these exercises 2-3 times daily with 10-15 repetitions can significantly strengthen the cervical region, promoting long-term pain relief and functional recovery. Consistency is key to achieving optimal results and maintaining spinal health.
Cervical Traction and Mobilization Techniques
Cervical traction and mobilization techniques are used to relieve pressure on compressed nerves, improving mobility and reducing pain. These methods enhance spinal alignment and promote healing.
4.1 Benefits of Cervical Traction
Cervical traction is a widely used technique in physical therapy to alleviate pain and discomfort caused by cervical radiculopathy. It works by gently stretching the cervical spine, reducing pressure on compressed nerves. This method can effectively relieve radiating arm pain, numbness, and tingling sensations. Regular use of cervical traction improves spinal alignment, enhances blood flow, and promotes healing. It is particularly beneficial for patients who experience persistent pain or limited mobility. When combined with strengthening exercises and manual therapy, cervical traction can significantly accelerate recovery and restore functional abilities.
4.2 Manual Therapy and Mobilization
Manual therapy and mobilization are essential components of physical therapy for cervical radiculopathy; Techniques such as joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, and nerve gliding focus on restoring normal movement and reducing stiffness in the cervical spine. These methods help alleviate nerve compression, improve range of motion, and enhance overall flexibility. Manual therapy also targets tight muscles and scar tissue, which can contribute to pain and limited mobility. By addressing these factors, mobilization techniques can significantly reduce symptoms and improve functional outcomes, making daily activities easier and less painful for patients.

Posture Correction and Body Mechanics
Proper posture reduces nerve compression and alleviates pain. Exercises like chin tucks and shoulder rolls improve spinal alignment and reduce strain on cervical muscles daily.
5.1 Importance of Proper Posture
Proper posture is essential for managing cervical radiculopathy, as it reduces nerve compression and muscle strain. Maintaining a neutral spine alignment minimizes pressure on the cervical nerve roots, alleviating pain and discomfort. Good posture involves sitting up straight with shoulders back, avoiding forward head positions, and keeping the chin level. Consistent postural awareness helps prevent recurrence of symptoms and promotes long-term spinal health. Incorporating postural exercises, such as chin tucks and shoulder rolls, strengthens the neck and shoulder muscles, further supporting proper alignment and reducing the risk of nerve irritation.
5.2 Exercises for Postural Awareness
Exercises for postural awareness are vital for improving spinal alignment and reducing cervical strain. Chin tucks help strengthen the neck muscles while maintaining proper head positioning. Shoulder rolls and thoracic extensions can reduce upper back stiffness and promote better posture. Pelvic tilts and cat-cow stretches enhance spinal flexibility and body awareness. These exercises should be performed 3-4 times daily to reinforce proper alignment. Practicing postural awareness exercises regularly can help prevent forward head posture, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate nerve irritation, ultimately supporting long-term spinal health and reducing cervical radiculopathy symptoms.
Progression of Exercises
Progression involves advancing to dynamic movements and functional activities, helping patients gradually return to daily life with improved strength and mobility.
6.1 Advanced Strengthening Techniques
Advanced strengthening techniques focus on improving the endurance and power of cervical and scapular muscles. These exercises, such as resisted cervical extensions and diagonal arm lifts, target deep neck flexors and scapular stabilizers. Progression may include dynamic movements and functional activities, ensuring proper form to avoid exacerbating symptoms. These exercises enhance posture, reduce pain, and improve overall neck function, preparing patients for daily activities and reducing the risk of recurrence. They are tailored to individual strength levels, promoting gradual and sustainable progress.
6.2 Functional Activities and Return to Daily Life
Functional activities aim to restore the ability to perform daily tasks comfortably. Techniques include posture correction, activity modification, and gradual reintroduction of movements. Patients learn to avoid positions or actions that strain the cervical spine. Strengthening exercises are combined with practical strategies to enhance mobility and reduce pain during activities like lifting, bending, or reaching. The goal is to help individuals resume normal functioning while minimizing the risk of recurrence. Consistent practice of these techniques ensures long-term management and improves overall quality of life.
Downloadable PDF Guide
A free downloadable PDF guide provides a comprehensive summary of exercises, treatment tips, and strategies for managing cervical radiculopathy. It offers easy-to-follow instructions for effective pain relief and functional restoration.
7.1 Summary of Exercises
The downloadable PDF guide includes a detailed summary of exercises tailored for cervical radiculopathy management. It features stretching techniques for cervical musculature, strengthening exercises to improve neck stability, and thoracic mobility exercises to reduce nerve compression. The guide also outlines isometric neck exercises, such as flexion, extension, and side bends, to enhance strength without strain. Additionally, it provides illustrations and instructions for proper posture correction and functional activities to aid in daily life. Each exercise is designed to alleviate pain, restore function, and prevent recurrence, offering a clear roadmap for long-term recovery and management.
7.2 Tips for Long-Term Management
For long-term management of cervical radiculopathy, maintaining proper posture and avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms are crucial. Regular exercise routines, including stretching and strengthening, should be continued to sustain neck stability. Monitoring progress and adjusting exercises as needed ensures optimal recovery. Patient education on body mechanics and ergonomics is essential to prevent relapse. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques and maintaining a healthy lifestyle further supports overall well-being. A consistent routine and adherence to professional guidance can significantly enhance long-term outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence, promoting a pain-free and active lifestyle. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are recommended for sustained care.
